National Health Service (NHS)
The largest public organisation in the world with over 2Million workforce. The NHS is a complex system, which can sometimes make it difficult to understand – especially working out who is responsible for what. It’s made up of a wide range of different organisations with different roles, responsibilities and specialties. These organisations provide a variety of services and support to patients and carers.
There’s more than one NHS in the UK
As the responsibility of health care has been passed from the UK government to the Scottish Government, Welsh Government, and Northern Irish Assembly. NHS England, NHS Wales (GIG Cymru), and NHS Scotland provide health care services in Great Britain.
The founding principles were that services should be comprehensive, universal and free at the point of delivery a health service based on clinical need, not ability to pay. Each service provides a comprehensive range of health services, free at the point of use for people ordinarily resident in the United Kingdom apart from dental treatment and optical care. In England, NHS patients have to pay prescription charges; some, such as those aged over 60 and certain state benefit recipients, are exempt.
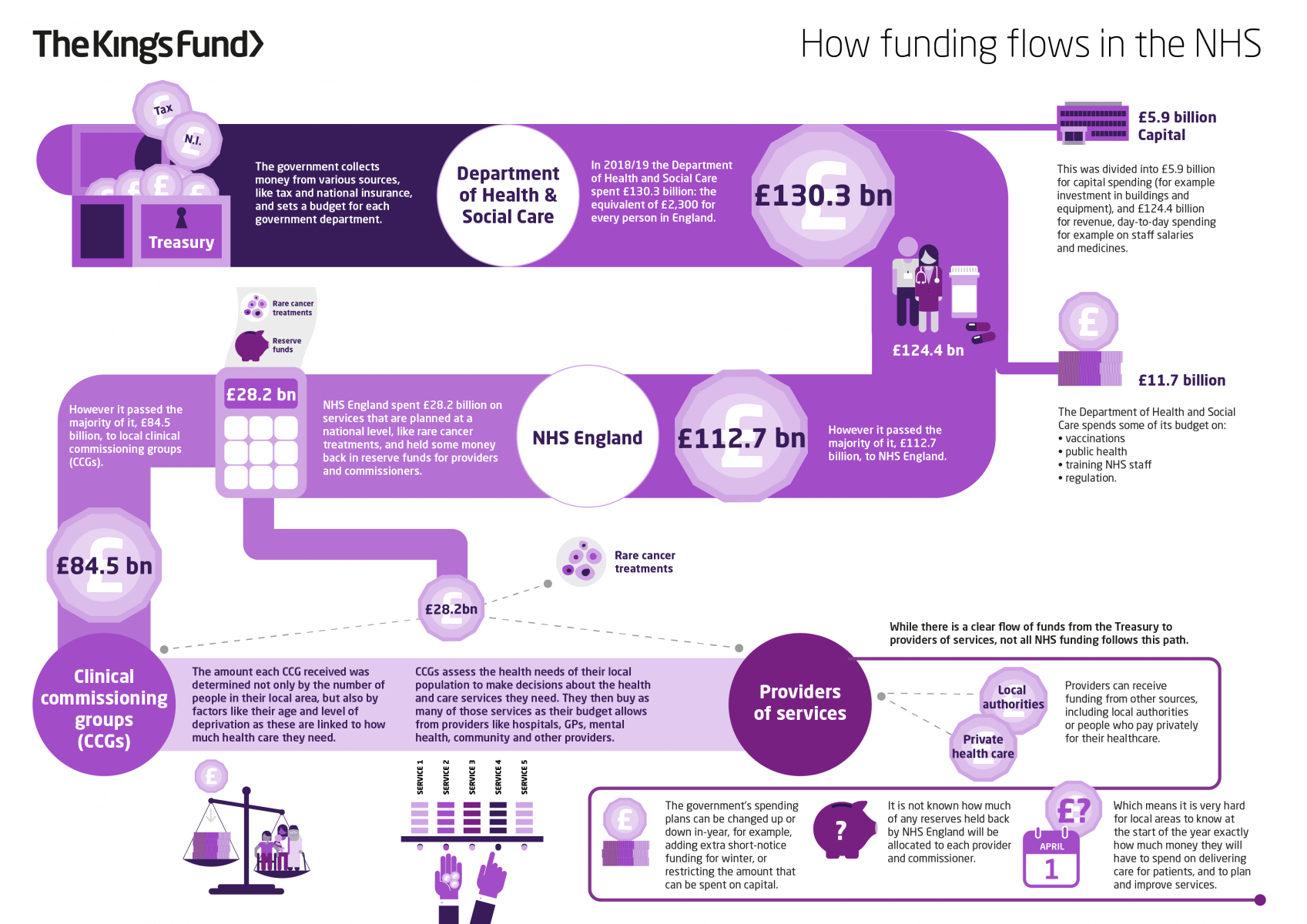
Employed around 1.6 million people with a combined budget of £136.7 billion
Taken together, the four National Health Services in 2015–2016 employed around 1.6 million people with a combined budget of £136.7 billion. In 2014, the total health sector workforce across the United Kingdom was 2,165,043. Every 24 hours it sees one million patients, and with 1.7 million staff it is the fifth biggest employer in the world, as well as the largest non-military public organisation in the world.
Several other countries either copy the United Kingdom’s model or directly rely on Britain’s assessments for their own decisions on state-financed drug reimbursements.
Health care services
It refers to the Government-funded medical and health care services that everyone living in the UK can use without being asked to pay the full cost of the service. These services include: